What Financial Freedom Really Means

The phrase financial freedom is often used lightly, to describe wealth, success, or escape from debt. But for us at BiorLabs, it means something deeper: the ability to control what you own, how you use it, and who has power over it.
Today, that control is quietly slipping away. Every transaction we make passes through intermediaries who decide when, how, and whether it can happen. We have normalised this dependence because we grew up inside it. The modern financial system functions, but it does so on its own terms, not ours.
At BiorLabs, we believe it is time to question that trade-off. True financial freedom is not about rejecting systems entirely, but about reclaiming choice within them: the ability to save, transact, and build value without asking for permission. It is the simple right to decide which parts of our financial lives remain ours.
This series begins with that idea: that finance should be built around and for people and that technology can be a path back to autonomy, not another layer of control.
From Trusting Institutions to Trusting Ourselves
The system we inherited was designed for a different time, when centralisation was the only way to coordinate trust. Banks held money, governments issued it, and processors like card networks ensured it could move. The trade-off was clear: stability in exchange for dependence.
But dependence has its limits. Intermediaries act as both enablers and gatekeepers. They monitor behaviour, collect personal data, and decide who gets access.
In 2022, thousands of people in Canada discovered that their bank accounts could be frozen by government order during the protest movement, even if they were never charged with a crime. In Lebanon, years of financial mismanagement led banks to limit withdrawals to a few hundred dollars per month, leaving citizens unable to access their life savings. And in Argentina, where inflation surpassed 200 percent in 2023, the national currency lost purchasing power faster than most people could convert it into something stable.
Additionally centralised authorities decide who can have access to financial tools. As of July 2024, nearly 1.4 billion adults worldwide remain unbanked, according to the World Bank. They cannot open accounts or make digital payments because they lack documents, income, or access to the right country or region.

These examples reveal a shared truth: centralised systems work for some, but less for others, and always at the cost of freedom and ownership.
But over the past decade, technology has shown that trust and financial services do not need to be centralised. With blockchain networks, individuals can hold assets directly, prove ownership cryptographically, and transact across borders transparently and without third-party approval. This shift, from trusting institutions to trusting code, is the foundation of self-custody.
Self-custody means that you hold your cryptographic private keys and, by extension, your funds. No intermediary can seize, freeze, or reassign what you own. It is a simple idea with profound implications: financial independence is no longer defined by a bank account, but by access to your own digital keys. It returns ownership and the freedom to transact directly to you.
Financial Freedom Is Also About Efficiency
Financial freedom is not only about ownership or privacy. It is also about efficiency: the ability to move value when and where it is needed, without friction, excessive fees, or endless intermediaries.
In traditional finance, even the simplest cross-border transaction can become a chain of approvals, verifications, and conversions. Transfers move slowly through correspondent banks, each taking a small share along the way. According to the World Bank, the global average cost of sending remittances stood at around 6.48 percent in 2025.
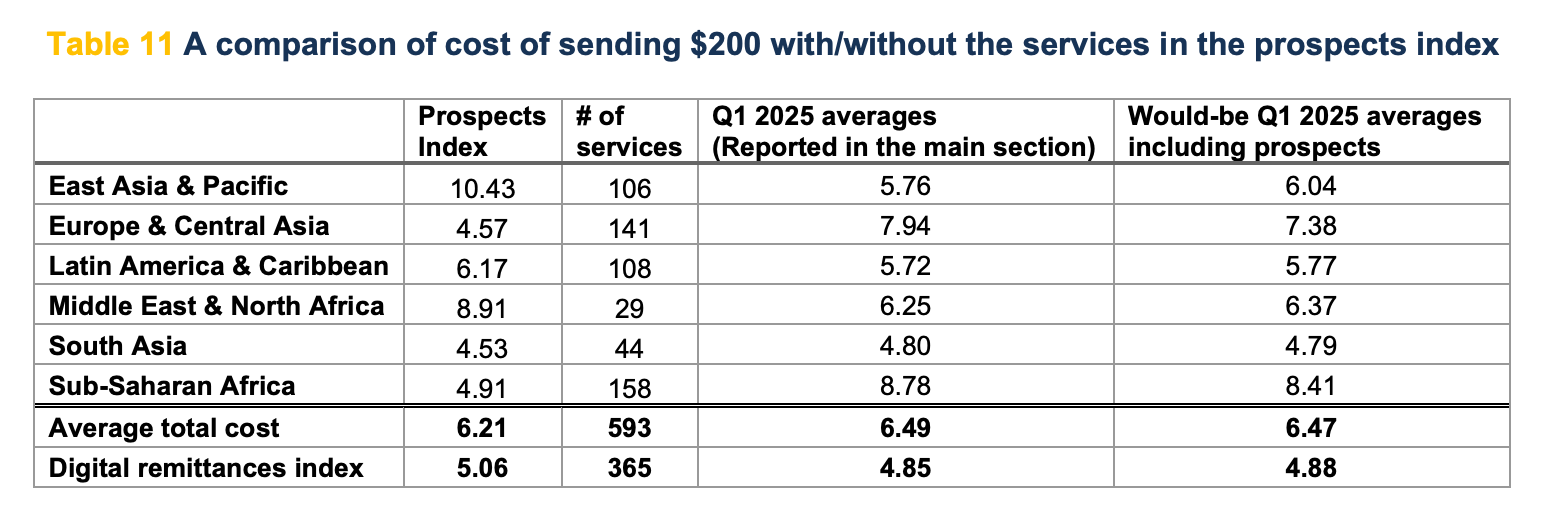
Beyond the cost, another issue is the uncertainty built into the process. International payments can take several days to settle. Funds are converted multiple times, moving through different currencies and clearing systems. Every layer introduces friction, delay, potential controls and exposure to risk. For small businesses and independent workers, these inefficiencies mean higher operating costs and reduced access to global markets.
The blockchain technology has already shown that transactions do not need to work this way. Digital ownership, open networks, and peer-to-peer transfers allow value to move directly between people, near-instantly, and with full transparency. For the first time, efficiency and autonomy can coexist.
Building the next era of FInancial Freedom
Still, freedom is only meaningful when it is usable. The technology exists, but much of it is still built for technically skilled users, not for everyday people. Interfaces are complex and sending and receiving assets across blockchains or between wallets can feel risky or confusing. Additionally, using these assets in the real world remains a challenge.
We believe the real task is not only building decentralised systems, but making them human. At BiorLabs, we see usability as a core form of freedom. People should be able to hold, send, and exchange value without technical barriers or surrendering control.
Our guiding principles are simple: Trust, Transparency, Security, and Innovation. They define not only what we build, but why we build it, to make financial autonomy accessible to everyone.



